Two complex numbers for which the real parts are equal and the imaginary parts are additive inverses. a + bi and a – bi are complex conjugates.
A number in the form a + bi, where a and b are real numbers and i is the square root of −1.
One binomial in a conjugate pair. Given the binomial a + b, the conjugate is a – b; given a – b, the conjugate is a + b.
A pair of binomials that, when multiplied, follow the pattern: ![]()
The product of a pair of binomials that are conjugates is the difference of two squares.
The number which, when multiplied together three times yields the original number. For example, the cube root of 64 is 4 because 4 • 4 • 4 = 64.
In the Quadratic Formula, the expression underneath the radical symbol: b2 – 4ac. The discriminant can be used to determine the number and type of solutions the formula will reveal.
A number in the form bi, where b is a real number and i is the square root of −1.
The imaginary term, bi, in a complex number a + bi.
The small positive integer just outside and above the radical symbol that denotes the root. For example, ![]() denotes the cube root.
denotes the cube root.
A trinomial that is the product of a binomial times itself, such as a2 + 2ab + b2 (from (a + b)2), and a2 – 2ab + b2 (from (a – b)2).
The positive square root of a number, as in ![]() . By definition, the radical symbol always means to find the principal root. Note that zero has only one square root, itself (since 0 • 0 = 0).
. By definition, the radical symbol always means to find the principal root. Note that zero has only one square root, itself (since 0 • 0 = 0).
The product of two or more non-zero numbers raised to a power equals the product of each number raised to the same power: (ab)x = ax • bx
For any real numbers a and b (b ≠ 0) and any positive integer x: 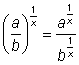
For any real numbers a and b (b ≠ 0) and any positive integer x: ![]()
The symbol, ![]() , used to denote the process of taking a root of a quantity.
, used to denote the process of taking a root of a quantity.
The real term, a, in a complex number a + bi.
A number that when multiplied by itself gives the original nonnegative number. For example, 6 • 6 = 36 and −6 • −6 = 36 so 6 is the positive square of 36 and −6 is the negative square root of 36.
If x2 = a2, then x = a or x = −a.