| addend | A number added to one or more other numbers to form a sum. |
| additive identity | The number 0 is called the additive identity because when you add it to a number, the result you get is the same number. For example, 4 + 0 = 4. |
| additive inverse | Any two numbers whose sum is zero, such as 3 and -3, because 3 + (-3) = 0. |
| arithmetic operations | The operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. |
| associative property of addition | For three or more real numbers, the sum is the same regardless of how you group the numbers. For example, (6 + 2) + 1 = 6 + (2 + 1). |
| associative property of multiplication | For three or more real numbers, the product is the same regardless of how you group the numbers. For example, (3 • 5) • 7 = 3 • (5 • 7). |
| base | The expression that is being raised to a power when using exponential notation. In 53, 5 is the base, which is the number that is repeatedly multiplied. 53 = 5 • 5 • 5. In ab, a is the base. |
| commutative property of addition | Two real numbers can be added in any order without changing the sum. For example, 6 + 4 = 4 + 6. |
| commutative property of multiplication | Two real numbers can be multiplied in any order without changing the product. For example, 8 • 9 = 9 • 8. |
| constant | A symbol that represents a quantity that cannot change. It can be a number, letter or a symbol. |
| counting numbers | Also called natural numbers, the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, ... |
| distribute | To rewrite the product of the number and a sum or difference using the distributive property. |
| distributive property of multiplication | The product of a sum (or a difference) and a number is the same as the sum (or difference) of the product of each addend (or each number being subtracted) and the number. For example, 3(4 + 2) = 3(4) + 3(2), and 3(4 – 2) = 3(4) – 3(2). |
| divisor | The number that you are dividing by in a division problem. In the problem 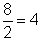 , 2 is the divisor. , 2 is the divisor. |
| evaluate | To find the value of an expression. |
| exponent | When a number is expressed in the form ab, b is the exponent. The exponent indicates how many times the base is used as a factor. Power and exponent mean the same thing. |
| exponential notation | A shorter way to write repeated multiplication. For example, 24 means 2 • 2 • 2 • 2. Two is used as a factor 4 times. |
| expression | A mathematical phrase that can contain a combination of numbers, variables, or operations. |
| factor | A number or mathematical symbol that is multiplied by another number or mathematical symbol to form a product. For example, in the equation 4 • 5 = 20, 4 and 5 are factors. |
| grouping symbols | Symbols such as parentheses, braces, brackets, and fraction bars that indicate the numbers to be grouped together. |
| identity property of 0 | When you add 0 to any number, the sum is the same as the original number. For example, 55 + 0 = 55. |
| identity property of 1 | When you multiply any number by 1, the product is the same as the original number. For example, 9(1) = 9. |
| integers | The numbers …, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3… |
| inverse operations | A mathematical operation that can reverse or “undo” another operation. Addition and subtraction are inverse operations. Multiplication and division are inverse operations. |
| irrational numbers | Numbers that cannot be written as the ratio of two integers—the decimal representation of an irrational number is nonrepeating and nonterminating. |
| multiplicative inverse | Two numbers are multiplicative inverses if their product is 1. For example, 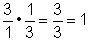 . . |
| natural numbers | Also called counting numbers, the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, … |
| negative numbers | Numbers less than 0. |
| nonrepeating decimals | Numbers whose decimal parts continue without repeating—these are irrational numbers. |
| nonterminating decimals | Numbers whose decimal parts continue forever (without ending in an infinite sequence of zeros)—these decimals can be rational (if they repeat) or irrational (if they are nonrepeating). |
| opposite | An opposite of a number is the number with the opposite sign, but same absolute value. For example, the opposite of 72 is -72. A number plus its opposite is always 0. |
| order of operations | The rules that determine the sequence of calculations in an expression with more than one type of computation. |
| positive number | Numbers greater than 0. |
| power | In an exponent ab, the power is represented by b. The power indicates how many times the base is used as a factor. Power and exponent mean the same thing. |
| quotient | The result of a division problem. In the problem 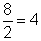 , 4 is the quotient. , 4 is the quotient. |
| rational numbers | Numbers that can be written as the ratio of two integers, where the denominator is not zero. |
| real numbers | All rational or irrational numbers. |
| reciprocal | A number that when multiplied by a given number gives a product of 1. For example, 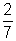 and and 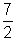 are reciprocals of each other. are reciprocals of each other. |
| repeating decimals | Numbers whose decimal parts repeat a pattern of one or more digits—these are all rational numbers. |
| set | A collection or group of things such as numbers. |
| substitute | The replacement of a variable with a number. |
| terminating decimals | Numbers whose decimal parts do not continue indefinitely but end eventually—these are all rational numbers. |
| variable | A letter or symbol used to represent a quantity that can change. |
| whole number | The numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, …., or all natural numbers plus 0. |
![]() , 2 is the divisor.
, 2 is the divisor.![]() .
.![]() , 4 is the quotient.
, 4 is the quotient.![]() and
and ![]() are reciprocals of each other.
are reciprocals of each other.