| coordinates | a pair of numbers that identifies a point on the coordinate plane—the first number is the x-value and the second is the y-value |
| dependent variable | a value or variable that depends upon the independent value |
| independent variable | a value or variable that changes or can be manipulated by circumstances |
| intercept | a point where a line meets or crosses a coordinate axis |
| linear equation | an equation that describes a straight line |
| linear function | a function with a constant rate of change and a straight line graph |
| parallel lines | lines that have the same slope and different y-intercepts |
| perpendicular lines | lines that have opposite reciprocal slopes |
| point-slope formula | a form of linear equation, written as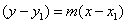 , where m is the slope and (x1, y1) are the co-ordinates of a point , where m is the slope and (x1, y1) are the co-ordinates of a point |
| rate of change | the constant in a proportional function equation; it describes the ratio or proportional relationship of the independent and dependent variables—also called the constant of variation or the constant of proportionality |
| rise | vertical change between two points |
| run | horizontal change between two points |
| slope | the ratio of the vertical and horizontal changes between two points on a surface or a line |
| slope formula | the equation for the slope of a line, written as 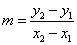 , where m is the slope and (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) are the coordinates of two points on the line , where m is the slope and (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) are the coordinates of two points on the line |
| slope-intercept form | a linear equation, written in the form y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept |
| slope-intercept formula | a linear equation, written as y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept |
| standard form of a linear equation | a linear equation, written in the form Ax + By = C, where x and y are variables and A, B, and C are integers |
| x-intercept | the point where a line meets or crosses the x-axis |
| y-intercept | the point where a line meets or crosses the y-axis |
![]() , where m is the slope and (x1, y1) are the co-ordinates of a point
, where m is the slope and (x1, y1) are the co-ordinates of a point![]() , where m is the slope and (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) are the coordinates of two points on the line
, where m is the slope and (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) are the coordinates of two points on the line