| absolute value | the value of a number without regard to its sign |
| Additive Inverse Property | states that every real number added to its additive inverse (or opposite) will equal zero: For all real numbers a, a + (-a) = 0; also called Inverse Property of Addition |
| coefficient | a number that multiplies a variable |
| common denominator | a number that is a multiple of all of the denominators in a group of fractions |
| Distributive Property | states that the product of a number and a sum equals the sum of the individual products of the number and the addends: for all real numbers a, b, and c, a(b + c) = ab + ac |
| equation | a statement that describes the equality of two expressions by connecting them with an equals sign |
| formula | a type of equation—usually reserved for multi-variable equations that describe a well-known or often repeated calculation |
| Inverse Operations | operations that undo or cancel one another, such as addition/subtraction and multiplication/division |
| multi-step equation | an equation that requires more than one step to solve |
| Multiplicative Inverse Property | states that any number multiplied by 1 over that number equals 1: For all real numbers a, 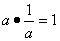 ; also called Inverse Property of Multiplication ; also called Inverse Property of Multiplication |
| numeric constant | a quantity that has a known, fixed value |
| operation | a mathematical procedure, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division |
| Property of Equality | states that the equality of an equation is maintained when both sides have the same value added, subtracted, multiplied, or divided |
| variable | a symbol that represents an unknown value |
![]() ; also called Inverse Property of Multiplication
; also called Inverse Property of Multiplication