| addend | A number added to one or more numbers to form a sum. |
| addition property of 0 | The sum of any number and 0 is equal to that number. The number 0 is often called the additive identity. |
| amount | In a percent problem, the portion of the whole corresponding to the percent. |
| associative law of addition | For three or more numbers, the sum is the same regardless of how you group the numbers. For example, (6 + 2) + 1 = 6 + (2 + 1). |
| associative law of multiplication | For three or more numbers, the product is the same regardless of how you group the numbers. For example, 3 • (5 • 7) = 3 • (5 • 7). |
| base | In a percent problem, the base represents how much should be considered 100% (the whole); in exponents, the base is the value that is raised to a power when a number is written in exponential notation. In the example of 53, 5 is the base. |
| capacity | The amount of liquid (or other pourable substance) that an object can hold when it's full. |
| Celsius | A measure of temperature commonly used in countries that use the metric system. On the Celsius scale, water freezes at 0° C and boils at 100° C. |
| common denominator | A number that is a multiple of all of the denominators in a group of fractions. |
| commutative law of addition | Two numbers can be added in any order without changing the sum. For example, 6 + 4 = 4 + 6. |
| commutative law of multiplication | Two numbers can be multiplied in any order without changing the product. For example, 8 • 9 = 9 • 8. |
| composite number | A natural number that has at least one factor other than 1 and itself. |
| cubing | Raising a number to a power of 3. 23 is read “2 to the third power” or “2 cubed,” and means use 2 as a factor three times in the multiplication. 23 = 2 • 2 • 2 = 8. |
| cup | A unit of capacity equal to 8 fluid ounces. |
| decimal fractions | A fraction written as a decimal point and digits to the right of the decimal point |
| decimal number | Decimal numbers are numbers whose place value is based on 10s, including whole numbers and decimal fractions, which have decimal points and digits to the right of the decimal point. The numbers 18, 4.12 and 0.008 are all decimal numbers. |
| denominator | The bottom number of a fraction that tells how many equal parts are in the whole. |
| difference | The quantity that results from subtracting one number from another, or from subtracting the subtrahend from the minuend. |
| digit | One of the symbols 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9. |
| distribute | To rewrite the product of the number and a sum or difference using the distributive property. |
| distributive property of multiplication over addition | The product of a number and a sum is the same as the sum of the product of the number and each of the addends making up the sum. For example, 3(4 + 2) = 3(4) + 3(2). |
| distributive property of multiplication over subtraction | The product of a number and a difference is the same as the difference of the product of the number and each of the numbers being subtracted. For example, 8(10 – 2) = 8(10) – 8(2). |
| dividend | The number to be divided up in a division problem. In the problem 8 ÷ 2 = 4, 8 is the dividend. |
| divisibility test | A rule that tells quickly whether dividing a number by another number can be done without leaving a remainder. |
| divisible | Can be divided by a number without leaving a remainder. For example, 20 is divisible by 4 because 20 ÷ 4 = 5 (no remainder). |
| divisor | The number that is being divided into the dividend in a division problem. In the problem 8 ÷ 2 = 4, 2 is the divisor. |
| equation | A mathematical sentence that shows that two expressions are equal. |
| equivalent fractions | Two or more fractions that name the same part of the whole. |
| estimate | An answer to a problem that is close to the exact number, but not necessarily exact. |
| even number | A whole number that is divisible by 2. |
| expanded form | A way to write a number as a sum of the value of its digits. For example, thirty-two is written in expanded form as 30 + 2, or 3 tens + 2 ones, or (3 • 10) + (2 • 1). |
| exponent | The number that indicates how many times the base is used as a factor. In the example of 53, 3 is the exponent and means that 5 is used three times as a factor: 5 • 5 • 5. |
| exponential notation | A notation that represents repeated multiplication using a base and an exponent. For example, 24 is notation that means 2 • 2 • 2 • 2. This notation tells you that 2 is used as a factor 4 times. 24 = 16. (Also called exponential form.) |
| expression | A mathematical phrase. For example, 8 • 2 + 3 is an expression. It represents the quantity 19. |
| factor | A number that is multiplied by another number or numbers to get a product. For example, in the equation 4 • 5 = 20, 4 and 5 are factors. |
| factor label method | One method of converting a measurement from one unit of measurement to another unit of measurement. In this method, you multiply the original measurement by unit fractions containing different units of measurement to obtain the new unit of measurement. |
| factor pair | A pair of numbers whose product is a given number. For example, 2 and 15 are a factor pair of 30 because 2 •15 = 30. Both 2 and 15 are factors of 30. |
| factor tree | A diagram showing how a number can be written as factors, and those factors written as a product of factors, and so on until only prime numbers are used. |
| Fahrenheit | A measure of temperature commonly used in the United States. On the Fahrenheit scale, water freezes at 32° F and boils at 212° F. |
| fluid ounce | A unit of capacity equal to 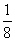 of a cup. One fluid ounce of water at 62°F weighs about one ounce. of a cup. One fluid ounce of water at 62°F weighs about one ounce. |
| foot | A unit for measuring length in the U.S. customary measurement system. 1 foot = 12 inches |
| fraction | An expression used to refer to a part of a whole. |
| gallon | A unit equal to 4 quarts, or 128 fluid ounces. |
| gram | The base unit of mass in the Metric system. |
| grouping symbols | Symbols such as parentheses, braces, brackets, and fraction bars that indicate the numbers to be grouped together. |
| improper fraction | A fraction in which the numerator is equal to or greater than the denominator. |
| inch | A unit for measuring length in the U.S. customary measurement system. 1 foot = 12 inches |
| inequality | A mathematical sentence that compares two numbers that are not equal. |
| inverse operation | A mathematical operation that can reverse or “undo” another operation. Addition and subtraction are inverse operations. Multiplication and division are inverse operations. |
| least common denominator | (LCD) The least, or smallest, number that is a multiple of all the denominators in a group of fractions. |
| least common multiple | (LCM) The least, or smallest, number that is a multiple of two or more numbers. |
| length | The distance from one end to the other or the distance from one point to another. |
| like denominators | Denominators that are the same. |
| liter | The base unit of volume in the Metric system. |
| lowest terms | A fraction is in lowest terms if the numerator and denominator have no common factors other than 1. |
| measurement | The use of standard units to find out the size or quantity of items such as length, width, height, mass, weight, volume, temperature or time. |
| meter | The base unit of length in the Metric system. |
| metric system | A widely used system of measurement that is based on the decimal system and multiples of 10. |
| mile | A unit for measuring length in the U.S. customary measurement system. 1 mile = 5,280 feet or 1,760 yards. |
| minuend | The number from which another number is subtracted. |
| mixed number | An expression in which a whole number is combined with a proper fraction. For example 5 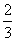 is a mixed number. |
| multiple | Any number that has a given number as a factor. For example, 4, 8, 16, and 200 are multiples of 4, because 4 is a factor of each of these numbers. |
| multiplication property of 1 | The product of any number and 1 is equal to that number. The number 1 is often called the multiplicative identity. |
| natural number | The numbers 1, 2, 3, 4 and so on. Also called counting numbers. |
| numerator | The top number of a fraction that tells how many parts of a whole are being represented. |
| operation | A mathematical process; the four basic operations are addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. |
| order of operations | The rules that determine the sequence of calculations in an expression with more than one type of computation. |
| ounce | A unit for measuring weight in the U.S. customary measurement system. 16 ounces = 1 pound. |
| percent | A ratio that compares a number to 100. “Per cent” means “per 100,” or “how many out of 100.” |
| perfect square | A whole number that can be expressed as a whole number raised to a power of 2. For example, 25 is a perfect square because 25 = 5 • 5 = 52. |
| perimeter | The distance around a two-dimensional shape. |
| period | Each group of three digits in a number separated by a comma. |
| pint | A unit of capacity equal to 16 fluid ounces, or 2 cups. |
| place value | The value of a digit based on its position within a number. |
| place-value chart | A chart that shows the value of each digit in a number. |
| polygon | A closed plane figure bounded by three or more line segments. |
| pound | A unit for measuring weight in the U.S. customary measurement system. 16 ounces = 1 pound. |
| power of 10 | Any whole number that can be represented by 10x. The first four powers of 10 are 1, 10, 100, and 1000. |
| prefix | A short set of letters that denote the size of measurement units in the Metric System. Metric prefixes include centi-, milli-, kilo-, and hecto-. |
| prime factorization | A number written as the product of its prime factors. |
| prime number | A natural number with exactly two factors: 1 and the number itself. |
| product | The result when two numbers are multiplied. For example, the product of 4 • 5 is 20. |
| proper fraction | A fraction in which the numerator is less than the denominator. |
| proportion | An equation that states that two ratios are equal. |
| quart | A unit of capacity equal to 32 fluid ounces, or 4 cups. |
| quotient | The result of a division problem. In the problem 8 ÷ 2 = 4, 4 is the quotient. |
| radical sign | The symbol used for square root and other roots. It looks like 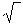 and the number is written under it. For example, the square root of nine is written with the radical sign: and the number is written under it. For example, the square root of nine is written with the radical sign: 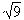 |
| raised to the power | When a base has an exponent, it can be said that the base is “raised to the power” of the exponent. For example, 35 is read as “3 raised to the 5th power.” |
| rate | A ratio that compares quantities measured in different units. For example, a speed compares the distance traveled to a length of time. |
| ratio | A comparison of two numbers by division. For example, the ratio of 15 boys in a class to 14 girls in the same class is 15:14. |
| reciprocal | A number that when multiplied by a given number gives a product of 1. For example, 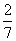 and and 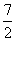 are reciprocals of each other. are reciprocals of each other. |
| regroup | Rewriting a number so you can subtract a greater digit from a lesser digit. |
| remainder | The amount left over after dividing a number. In the problem 11 ÷ 4 = 2 R3, 3 is the remainder. |
| rounding | Finding a number that’s close to a given number, but is easier to think about. |
| simplest form | A fraction is in simplest form if the numerator and denominator have no common factors other than 1. |
| square root | A value that can be multiplied by itself to give the original number. For example if the original number is 9, then 3 is its square root because 3 multiplied by itself (32, pronounced "3 squared") equals 9. The symbol used for a square root is called a radical sign and goes on top of the number. The square root of 9 is written as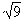 . . |
| squaring | Multiplying a number by itself, or raising the number to a power of 2. 82 can be read as “8 to the second power,” “8 to a power of 2,” or “8 squared.” |
| standard form | A way to write a number using digits. For example, thirty-two is written in standard form as 32. |
| subtrahend | The number that is subtracted from another number. |
| sum | The result when two or more numbers are added; the quantity that results from addition. |
| ton | A unit for measuring the weight of heavier items in the U.S. customary measurement system. 1 ton = 2,000 pounds. |
| trailing zero | A placeholder 0 that occurs after the final non-0 digit in a decimal number. In the number 22.0900, the 0s in the thousandths and ten-thousandths places are trailing zeros. |
| U.S. customary measurement system | The most common system of measurement used in the United States. It is based on English measurement systems of the 18th century. |
| unit equivalents | Statements of equivalence between measurement units within a system or in comparison to another system of units. For example 1 foot = 12 inches or 1 inch = 2.54 centimeters are both examples of unit equivalents. |
| unit fractions | A fraction where the numerator and denominator are equal amounts, as in 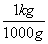 or or 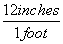 . Unit fractions serve to help with conversions in the Factor Label method. . Unit fractions serve to help with conversions in the Factor Label method. |
| unit of measurement | A standard amount or quantity. For example, an inch is a unit of measurement. |
| unit price | A rate in which the quantity is expressed as one unit. If 12 candy bars cost $24, the unit price is $2 per 1 candy bar. |
| unit rate | A rate in which the second quantity is one unit. If a bird flaps its wings 240 times in 3 minutes, the unit rate of wing flapping is 80 flaps per 1 minute. |
| unlike denominators | Denominators that are different from each other. For example the fractions 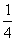 and and 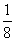 have different denominators, one denominator being 4 and the other denominator being 8. have different denominators, one denominator being 4 and the other denominator being 8. |
| weight | A mathematical description of how heavy an object is. |
| whole number | Any of the numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on. |
| yard | A unit for measuring length in the U.S. customary measurement system. 1 yard = 3 feet or 36 inches. |
![]() of a cup. One fluid ounce of water at 62°F weighs about one ounce.
of a cup. One fluid ounce of water at 62°F weighs about one ounce.![]()
![]() and the number is written under it. For example, the square root of nine is written with the radical sign:
and the number is written under it. For example, the square root of nine is written with the radical sign: ![]()
![]() and
and ![]() are reciprocals of each other.
are reciprocals of each other.![]() .
.![]() or
or ![]() . Unit fractions serve to help with conversions in the Factor Label method.
. Unit fractions serve to help with conversions in the Factor Label method.![]() and
and ![]() have different denominators, one denominator being 4 and the other denominator being 8.
have different denominators, one denominator being 4 and the other denominator being 8.