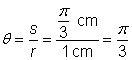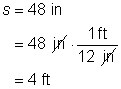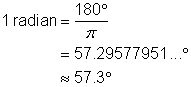Degree and Radian Measure
Learning Objective(s)
· Understand radian measure.
· Convert from degree to radian measure.
· Convert from radian to degree measure.
Introduction
You know that there can be different units of measurement to measure the same thing. For example, length can be measured in feet and meters and temperature can be measured in degrees Celsius and degrees Fahrenheit. We often use formulas to convert between different units of measurement.
There are also two ways to measure angles. You know how to measure them in degrees. Now you will learn how to measure them in radians and how to convert between these two measurements. While degree measure is used in everyday activities such as building construction and surveying land, radian measure is used for many calculations, such as the speed and distance traveled by satellites above the Earth’s surface—including the International Space Station! It is important to be able to measure angles in radians as well as in degrees and to be able to convert between the two systems.
In order for us to be able to define radians, it is necessary to introduce the concept of a central angle. A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle. In the circle below, the center is point O, the length of the radius is r, and ![]() is a central angle.
is a central angle.
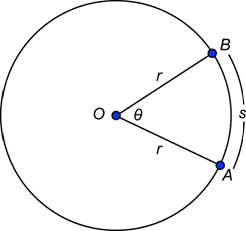
Notice that ![]() cuts off or determines an arc
cuts off or determines an arc ![]() that has length s. The radian measure of a central angle, often denoted by the Greek letter theta (
that has length s. The radian measure of a central angle, often denoted by the Greek letter theta (![]() ), is defined to be the ratio of the arc length to the length of the radius. So the radian measure of
), is defined to be the ratio of the arc length to the length of the radius. So the radian measure of ![]() is given by:
is given by:
![]()
Arc length, s, and radius, r, must be in the same units.
| Example | ||
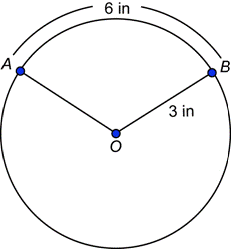
| Problem | What is the radian measure of central angle AOB?
| |
|
|
| In this circle, |
| Answer | The measure of central angle AOB is 2 radians. | |
| Example | ||
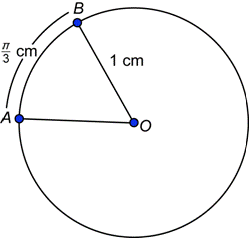
| Problem | Find the measure of central angle AOB in radians.
| |
|
|
| In this circle, |
| Answer | The measure of central angle AOB is | |
What is the connection between degrees and radians? Let’s see what happens when the arc is the entire circle:
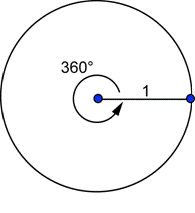
The circumference of this circle is given by ![]() . This is the arc length of the entire circle, or the arc length corresponding to a central angle of 360°. What is the radian measure of this angle?
. This is the arc length of the entire circle, or the arc length corresponding to a central angle of 360°. What is the radian measure of this angle?
![]()
A central angle of 360° has a radian measure of ![]() . That is:
. That is:
![]()
If you divide both sides by 2, you will obtain:
![]()
We’ll use this to convert from degrees to radians and vice versa.
While degrees are always written with a degree symbol (°), radians are usually written without any symbol or unit attached. So, for example, ![]() means the tangent of an angle that measures 3°, while
means the tangent of an angle that measures 3°, while ![]() means the tangent of an angle that measures 3 radians.
means the tangent of an angle that measures 3 radians.
Make sure that you use the same units of length for the length of the radius r and the arc length s. In the first example, they were both in inches; in the second example, they were both in centimeters. When you divide, those units cancel, and you are left with a unitless number.
| Example | ||
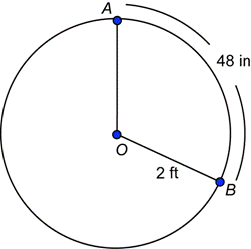
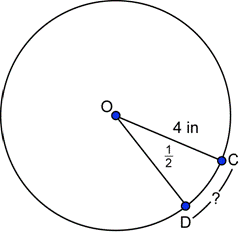
| Problem | Find the measure of central angle AOB in radians.
| |
|
|
| You want the arc length and the radius to have the same units, but they are given to you in inches and feet. You could convert either one. The arc determined by |
|
|
| In this circle, |
| Answer | The measure of central angle AOB is 2 radians. | |
If you take the definition of radian measure, ![]() , and multiply both sides by r, you get the formula for arc length:
, and multiply both sides by r, you get the formula for arc length:
![]()
| Example | ||
| Problem | The central angle shown has a measure of
| |
|
|
| In this circle, |
| Answer | The length of | |
We have used ![]() and
and ![]() to find the radian measure of the central angle as well as the arc length. But you can also use the arc length formula to find the length of the radius, as seen in the following example.
to find the radian measure of the central angle as well as the arc length. But you can also use the arc length formula to find the length of the radius, as seen in the following example.
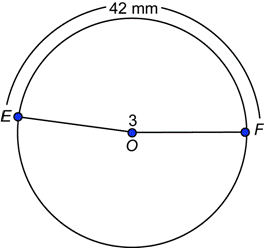
| Example | ||
| Problem | If the length of
| |
|
|
| You are given that |
|
|
| Solve the equation for r. |
|
|
| Rewrite as a mixed number. |
| Answer | The radius of the circle is 14 mm. | |
| A circle has a radius of 8 inches and central angle AOB makes an arc AB of length 2 feet.
What is the radian measure of angle AOB?
A) B) C) 3 D) 4
|
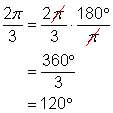
Earlier we saw that ![]() . Divide both sides of this equation by 180. You get:
. Divide both sides of this equation by 180. You get:
![]()
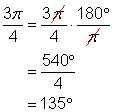
You can use this to convert the measure of an angle from degrees to radians. For example, if you wanted to convert 30° to radians, you could multiply both sides by 30:
![]()
To say this another way, you multiply 30° by ![]() to get
to get ![]() .
.
To convert 60° to radians, you multiply 60° by ![]() to get
to get ![]() .
.
In a similar fashion, multiply any degree measure by ![]() to convert it to radians.
to convert it to radians.
| Example | ||
| Problem | Convert 0°, 45°, and 90° to radians. | |
|
|
| In each case, just multiply by |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Answer |
| |
Here is a chart with the angles that we have converted so far.
Degree Measure | Radian Measure |
| 0° | 0 |
| 30° |
|
| 45° |
|
| 60° |
|
| 90° |
|
| 180° |
|
| 360° |
|
Here is the same information, with some additional angles, in a picture format:
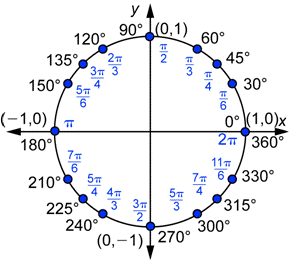
The same procedure works just as well for negative angles. Remember that a negative angle is just an angle that is oriented clockwise when drawn in standard position. A negative number of degrees becomes a negative number of radians.
| How many radians are there in
A) B) C) D)
|
Suppose you had angles measured in radians and you wanted to know their degree measure. The procedure is similar to the one going from degrees to radians.
Again, you know that ![]() . Divide both sides of this equation by
. Divide both sides of this equation by ![]() . You get:
. You get:
![]()
If you wanted to convert ![]() radians to degrees, you could multiply both sides of the above equation by
radians to degrees, you could multiply both sides of the above equation by ![]() :
:
![]()
To state this in another way, we multiplied ![]() by
by ![]() to get 30°. In a similar fashion, multiply any radian measure by
to get 30°. In a similar fashion, multiply any radian measure by ![]() to convert it to degrees.
to convert it to degrees.
| Example | ||
| Problem | Convert | |
|
|
| In each case, just multiply by |
|
|
|
|
| Answer |
|
|
Make sure that your answer has a degree symbol. An angle measure written without a degree symbol is always assumed to be in radians.
Here is a chart showing equivalent radian and degree measures for some common angles.
Radian Measure | Degree Measure |
| 0 | 0° |
|
| 30° |
|
| 45° |
|
| 60° |
|
| 90° |
|
| 180° |
|
| 360° |
| Example | ||
| Problem | Convert 1 radian to degrees and give your answer to the nearest tenth of a degree. | |
|
|
| Actually, you already know the value of 1 radian in degrees. However, you need to use a calculator to do the division and obtain a decimal. |
| Answer |
|
|
So 1 radian is a little less than 60°, or a little less than one-sixth of a circle.
You can use the same procedure for negative angles.
| What is the equivalent degree measure of
A) 150° B) C) D)
|
Summary
Angles can be measured in two ways: with degrees and radians. Radian measure of a central angle is defined as the ratio of the arc length to the length of the radius. This definition leads to the arc length formula: ![]() .
.
Radians and degrees are connected by the relationship ![]() . If you wish to convert from degrees to radians, multiply the degree measure by
. If you wish to convert from degrees to radians, multiply the degree measure by ![]() . If you wish to convert from radians to degrees, multiply the radian measure by
. If you wish to convert from radians to degrees, multiply the radian measure by ![]() .
.